
Understanding Anxiety and Its Impact on Daily Life
Anxiety is a natural physiological and psychological response to stress, characterized by feelings of unease, worry, or fear. While it is a normal and often beneficial reaction, particularly in challenging situations, anxiety can become overwhelming and debilitating when experienced frequently or intensely. There are various types of anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobias. Each disorder presents unique symptoms but shares common threads of excessive worry and fear.
The impact of anxiety on daily life can be profound. Individuals grappling with anxiety may experience a range of physical symptoms, such as a rapid heartbeat, fatigue, muscle tension, and gastrointestinal issues. Emotionally, they may face persistent feelings of impending doom, irritability, or the inability to concentrate. This emotional distress can interfere with personal relationships, work responsibilities, and overall quality of life. Moreover, the cycle of anxiety can create a feedback loop; heightened stress often leads to increased avoidance behaviors, further exacerbating the feelings of anxiety.
Understanding the causes and triggers of anxiety is crucial in managing it effectively. Factors such as genetics, brain chemistry, personality traits, and life events can contribute to the development of anxiety disorders. Common triggers include work pressures, relationship conflicts, and significant life changes. Given the pervasive nature of anxiety, it is vital to prioritize mental health and explore strategies that can help mitigate anxiety’s effects. Effective management can lead to improved well-being, enabling individuals to engage fully in daily activities and enjoy a fulfilling life.
The Science Behind Breathing Exercises and Anxiety Relief

The intricate connection between physiological processes and psychological states manifests clearly in the context of anxiety relief through breathing exercises. When an individual experiences anxiety, the body enters a heightened state of alertness characterized by increased heart rate, shallow breathing, and elevated levels of stress hormones. Conversely, engaging in controlled breathing practices can stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system, a critical component that counters these stress responses, promoting relaxation and a sense of calm.
Breathing exercises such as diaphragmatic breathing, box breathing, and deep, slow breathing have been shown to induce a physiological relaxation response. By consciously altering one’s breathing patterns, individuals can effectively lower heart rates and reduce blood pressure. This physiological shift helps to shift the body away from the sympathetic “fight or flight” response, which is often exacerbated during moments of anxiety, towards a more balanced state of homeostasis.
Numerous scientific studies support the efficacy of these simple breathing techniques in managing anxiety levels. Research published in journals like the Journal of Clinical Psychology and the International Journal of Yoga has highlighted that patients practicing regular breath control report significant decreases in anxiety symptoms. These studies suggest that integrating breathing exercises into daily routines not only improves immediate reactions to anxiety-inducing situations but also fosters long-term resilience against stress. Furthermore, the regular practice of these techniques is associated with a better overall mental well-being.
Incorporating breathing exercises into one’s daily life can essentially equip individuals with a practical tool for anxiety management. By understanding the physiological and psychological mechanisms at play, users of these methods can appreciate their potential to promote a calmer state of mind in the face of daily pressures.
Simple Breathing Exercises to Calm Anxiety: Step-by-Step Guides
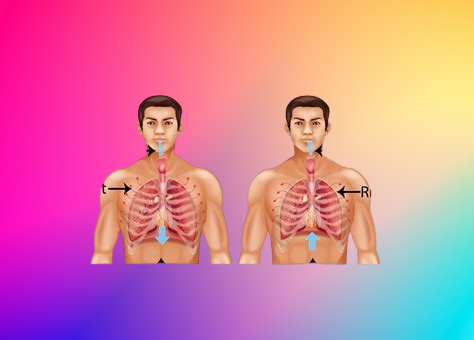
Breathing exercises can serve as an effective tool to calm anxiety and promote relaxation. Below are some simple techniques including diaphragmatic breathing, the 4-7-8 technique, and box breathing, complete with step-by-step instructions.
Diaphragmatic Breathing: This technique focuses on the diaphragm, helping to use the lungs more effectively.
Find a comfortable position, either sitting or lying down.
Place one hand on your chest and the other on your abdomen.
Inhale deeply through your nose for a count of four, ensuring that your diaphragm expands and your abdomen rises.
Hold your breath for a count of four.
Exhale slowly through your mouth for a count of six, feeling your abdomen fall.
Repeat for several minutes, allowing your body to relax with each breath.
4-7-8 Technique: This method is designed to promote relaxation and reduce anxiety.
Begin in a comfortable position, ensuring your back is straight.
Inhale quietly through your nose for four counts.
Hold your breath for seven counts.
Exhale completely through the mouth, making a whoosh sound, for eight counts.
Repeat this cycle a minimum of four times.
Box Breathing: This technique involves four equal parts, which can bring about a sense of calm.
Inhale through your nose for four counts.
Hold your breath for four counts.
Exhale through your mouth for four counts.
Hold your breath again for four counts.
These exercises can be practiced anywhere—whether at your desk, in your car, or before a meeting—offering flexibility to suit your needs. Customized options might include adjusting the count to a level that feels comfortable or integrating visualization techniques to enhance relaxation. Engaging in these practices during moments of heightened anxiety can effectively ground you in the present and promote a sense of serenity.
Incorporating Breathing Exercises into Your Daily Routine

Breathing exercises are a powerful tool for managing anxiety, but their effectiveness greatly depends on regular practice. To make these exercises a natural part of daily life, one needs to strategically incorporate them into routines. One common challenge individuals face is finding the time amidst busy schedules. However, these exercises can be seamlessly integrated at various points throughout the day.
Consider beginning the day with a few minutes of deep breathing after waking up. This practice can set a positive tone for the day ahead and help individuals enter a mindful state. Alternatively, taking short breaks during work or study sessions can serve as ideal moments to practice breathing exercises. Setting reminders on smartphones can be particularly helpful in establishing this habit, prompting a few minutes of focused breathing to alleviate stress as needed.
Another effective strategy is to connect breathing exercises with existing habits. For instance, practicing these techniques during daily activities such as waiting for public transport, during lunch breaks, or even while commuting can foster mindfulness without requiring additional time commitments. Identifying triggers for anxiety throughout the day can also be beneficial; when faced with such moments, individuals can turn to their breath as a grounding response.
Creating a peaceful environment when practicing breathing exercises can enhance their calming effects. Finding a quiet space, limiting distractions, and even incorporating elements such as soothing music or aromatherapy can lead to a more immersive experience. Consistency in practicing breathing exercises not only aids in immediate anxiety relief but also builds resilience over time. With regular practice, individuals can cultivate a more profound sense of well-being, enabling them to navigate daily challenges with greater ease and calmness.



[…] Organizing your home can play a significant role in reducing stress levels by creating spaces that promote calmness and clarity. Start by assessing each area of your home, focusing on areas that often contribute to feelings of overwhelm. A systematic approach to decluttering is vital; begin with one room at a time. Consider employing the “four-box method,” which involves using boxes labeled as keep, donate, trash, and relocate. This method helps in categorizing belongings, making the decluttering process more manageable and efficient. […]
[…] Lifestyle choices also critically influence mental health. Factors such as poor diet, lack of physical activity, and inadequate sleep can contribute to the development or worsening of depression. A sedentary lifestyle, in particular, is associated with lower mood and energy levels, while a balanced diet rich in nutrients can enhance overall mental well-being. Additionally, substance abuse, including the use of drugs and alcohol, is linked to higher instances of depressive symptoms. These substances often mask underlying issues and can lead to a cycle of dependency and further mental health deterioration. […]